The First WARNING of Allergies in Your Child
If your child has dry, itchy skin that won’t go away, it might not just be sensitive skin—it could be the first warning sign of allergies.

Atopic dermatitis, or eczema, is often the earliest clue that a child has an overactive immune system. It’s the first step of what doctors call the Allergic March—a progression where eczema can lead to food allergies, allergic rhinitis (hay fever), and even asthma. But here’s the good news: you can take action early to slow down or even stop this process.
Why Eczema Is More Than Just a Skin Problem

Think of your child’s skin as a protective shield. When it’s healthy, it locks in moisture and keeps irritants out. But with eczema, this barrier is weakened, allowing allergens, bacteria, and irritants to sneak in. This leads to inflammation, itching, and an even bigger risk of developing allergies later on.
So, what can you do? Strengthen that skin barrier! And science proves it works.
Can a Moisturizer Really Prevent Allergies? Science Says Yes!
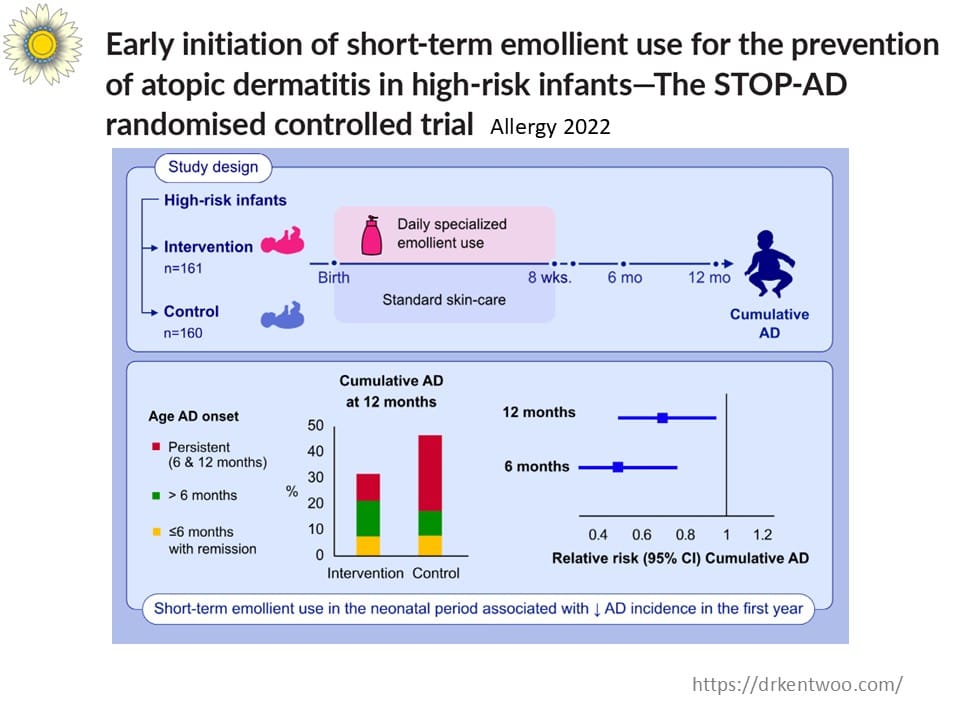
A groundbreaking study, the STOP-AD trial, found that simply applying a good moisturizer early in life can prevent eczema—and possibly even stop the Allergic March before it starts. That’s a game-changer.
But not just any moisturizer will do. You need something that’s gentle, deeply hydrating, and free from irritating preservatives
NatureDr8: An Ideal Choice for Eczema-prone Skin

✅ Strengthens the skin barrier – Packed with a prebiotic lipid complex that nourishes good skin bacteria, keeping harmful ones in check.
✅ Locks in moisture – Formulated with sacha inchi oil and sunflower oil, which are rich in skin-loving omega fatty acids.
✅ Safe for sensitive skin – 100% natural, fragrance-free, and preservative-free, making it perfect for babies and children with eczema.
Applying NatureDr8 daily is like giving your child’s skin an extra layer of protection—keeping moisture in and allergens out.
Gut Health & Allergies: Why Probiotics Matter

You might not think gut health has anything to do with eczema—but it does! A balanced gut microbiome plays a huge role in regulating the immune system and reducing allergy risk.
This is where Duoflora probiotics come in. It contains two powerful strains that have been clinically studied for allergy prevention:
🔹 Bifidobacterium breve M-16V – Helps regulate immune responses and reduces inflammation in allergic conditions like eczema.
🔹 Lactobacillus rhamnosus GG – One of the most researched probiotic strains for reducing eczema severity and lowering allergy risk.
By supporting a healthy gut, Duoflora helps strengthen your child’s natural defenses, making them less prone to eczema and other allergies.
What You Can Do Today to Stop the Allergic March

You don’t have to wait for allergies to develop—you can take steps right now to protect your child’s skin and immune system.
✔ Moisturize daily with NatureDr8 to build a strong skin barrier.
✔ Support gut health with Duoflora probiotics for allergy prevention.
✔ Identify triggers early with allergy testing.
✔ Minimize exposure to allergens like dust mites, pet dander, and harsh soaps.
Eczema doesn’t have to be the start of lifelong allergies. The earlier you take action, the better the chances of preventing the progression to more severe allergic conditions.
Want to learn more? Click to read and to download our eczema care guide: Essential Guide to Managing Atopic Dermatitis
If you need help – Contact us and Let Us Help you Take Control!