Urticaria or Hives: The Devil’s Itch That Won’t Let You Rest
Have you ever felt an itch so intense that it felt unbearable? Many people with urticaria, also known as hives, describe it as the Devil’s Itch—a relentless, burning sensation that spreads across the body in raised, red welts. The rash can start as a small bump, like a mosquito bite, but can quickly enlarge and spread, forming what some of my patients call a “map” on their skin.
Key Features of Urticaria (Hives)
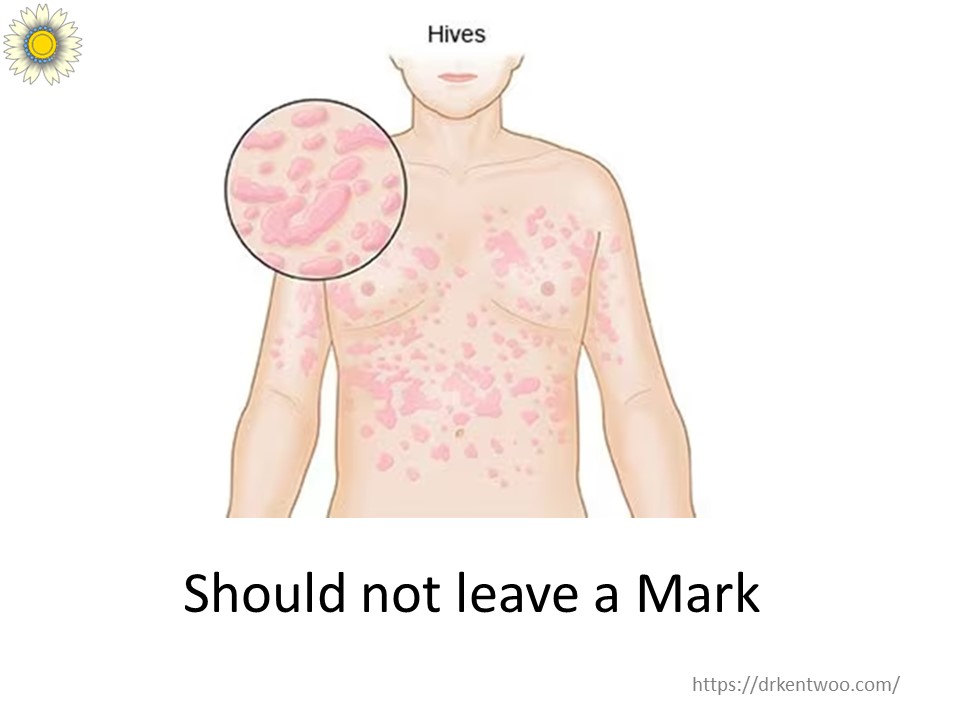
✔ Comes and goes within 24 hours – Each rash appears suddenly and fades within a day, though new ones may continue to develop.
✔ Varied appearances – Some hives look like raised mosquito bites (wheals), while others appear as flat, red patches.
✔ Affects any part of the body – Arms, legs, face, scalp, and even inside the mouth or throat.
✔ No lasting marks – Once the hives disappear, they don’t leave behind dark spots. (If a rash leaves a stain, it may suggest urticarial vasculitis, which needs further evaluation.)
When Hives Cause Swelling (Angioedema)
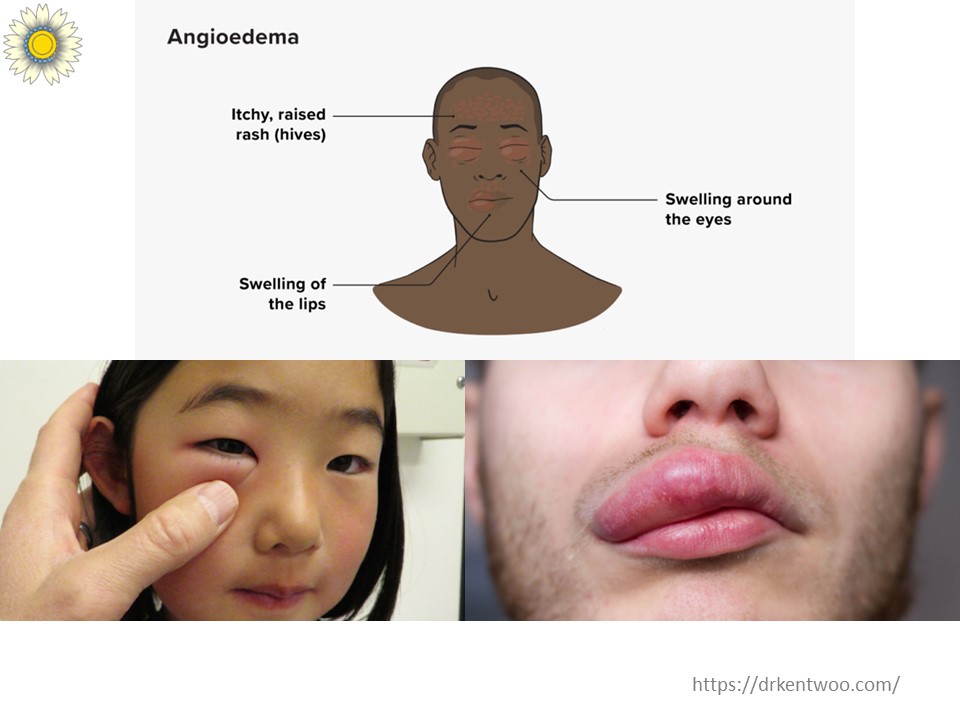
In more severe cases, urticaria can cause deep swelling, known as angioedema, particularly around the eyes, lips, and even the throat. This swelling can feel tight, uncomfortable, and may take hours to subside. In rare cases, it can lead to breathing difficulties, which require urgent medical attention.
What Causes Urticaria?
Hives can have many triggers, making them unpredictable and frustrating. Here are some common causes:
🔹 Acute allergic reactions – Foods (e.g., nuts, shellfish, dairy) or medications (e.g., antibiotics, painkillers) can cause sudden outbreaks.
🔹 Insect stings and bites – Bee, wasp, and fire ant stings can trigger hives, sometimes leading to anaphylaxis, a life-threatening allergic reaction.
🔹 Viral infections – In both children and adults, viral illnesses can trigger hives, even without an allergy.
🔹 Chronic urticaria – If hives last for more than six weeks, an autoimmune condition could be the cause. In these cases, high-dose antihistamines (up to 4x the normal dose) may be needed to control symptoms.
Why do we emphasize achieving control over urticaria?
Because medical data and our experience shows that complete control not only provides relief but also increases the likelihood of long-term remission.
In other words, by managing your symptoms effectively now, we can help you achieve lasting freedom from this condition.
🔎 Learn more: [Autologous Therapy as Treatment for Chronic Urticaria]
When to See an Allergist/Immunologist
If you’re experiencing recurrent or severe urticaria, don’t ignore it. Proper evaluation by an Allergist/Immunologist can help identify triggers and develop a treatment plan.
The Allergy Immunology Clinic is here to help. If hives are making your life miserable, let’s find a solution together.
📅 Book a consultation today and take control of your symptoms!