Treating Allergies: A Comprehensive Approach

As an allergist and immunologist, I often meet families overwhelmed by allergies. One scenario I see time and time again:
Parents bring in their older child, who has severe eczema and food allergies. Lately, they’ve noticed wheezing—an early sign of asthma. Then, they glance at their newborn, who only has mild eczema (for now), and ask the big question:
👉 “Will my younger child develop the same severe allergies?”
I see the exhaustion on their faces—the sleepless nights managing eczema flares, the stress of checking every food label, and the anxiety of introducing new foods. They want to protect their younger child from the same struggles, but they don’t know where to start.
Taking care of families like these has shaped my approach to allergy treatment. I see three essential pillars of allergy management:
1. Prevention: Stopping Allergies Before They Start

Preventing allergies is possible, and early intervention makes all the difference. This includes:
✅ Introducing allergenic foods early – Studies show that delaying allergenic foods increases the risk of food allergies.
✅ Reducing exposure to allergens – Managing dust mites, pet dander, and environmental triggers helps prevent worsening allergies.
✅ Strengthening the gut microbiome – A healthy gut microbiome plays a key role in immune balance and allergy prevention.
This is why I helped develop Duoflora, a probiotic specifically designed to support immune health and reduce allergy risk by promoting a balanced microbiome.
2. Symptom Control: Achieving Maximum Quality of Life with Minimal Medication
While allergy medications don’t cure allergies, they play a critical role in improving quality of life by controlling symptoms and inflammation. However, many patients struggle with ongoing symptoms despite taking medications—or find themselves relying on too many medications without proper guidance.
As an allergist, my goal is not just to prescribe medication, but to tailor the right treatment plan so you can live with minimal symptoms while using the least amount of medication necessary. The right approach can mean the difference between:
🔹 Constant congestion vs. breathing freely
🔹 Uncontrolled asthma flares vs. exercising without worry
🔹 Waking up sneezing every morning vs. restful, uninterrupted sleep
By optimizing medication use, I help patients achieve long-term control while avoiding over-reliance on unnecessary treatments. If medications aren’t enough or symptoms keep getting worse, that’s a sign we need to take the next step.
3. Immune System Modulation: The Only Long-Term Solution
Allergen Immunotherapy: The Only Treatment That Changes the Immune System
Unlike medications that only mask symptoms, allergen immunotherapy (AIT) retrains the immune system. By gradually exposing the body to allergens in controlled doses, AIT teaches the immune system to stop overreacting.
💡 Why Choose Allergen Immunotherapy?
✅ Prevents new allergies from developing – Reduces the risk of becoming allergic to more things over time.
✅ Provides long-term relief – Many patients experience lasting benefits even after stopping treatment.
✅ Reduces medication use – Many patients find they need fewer medications or none at all.
✅ Prevents allergic disease progression – Can stop allergic rhinitis from turning into asthma.
I’ve seen remarkable transformations in my patients:
✔️ Severe asthma patients who once required frequent hospitalizations now manage well with occasional inhaler use.
✔️ Pet-allergic patients who couldn’t be around their pets can now live with them comfortably with minimal symptoms.
Two Forms of Immunotherapy
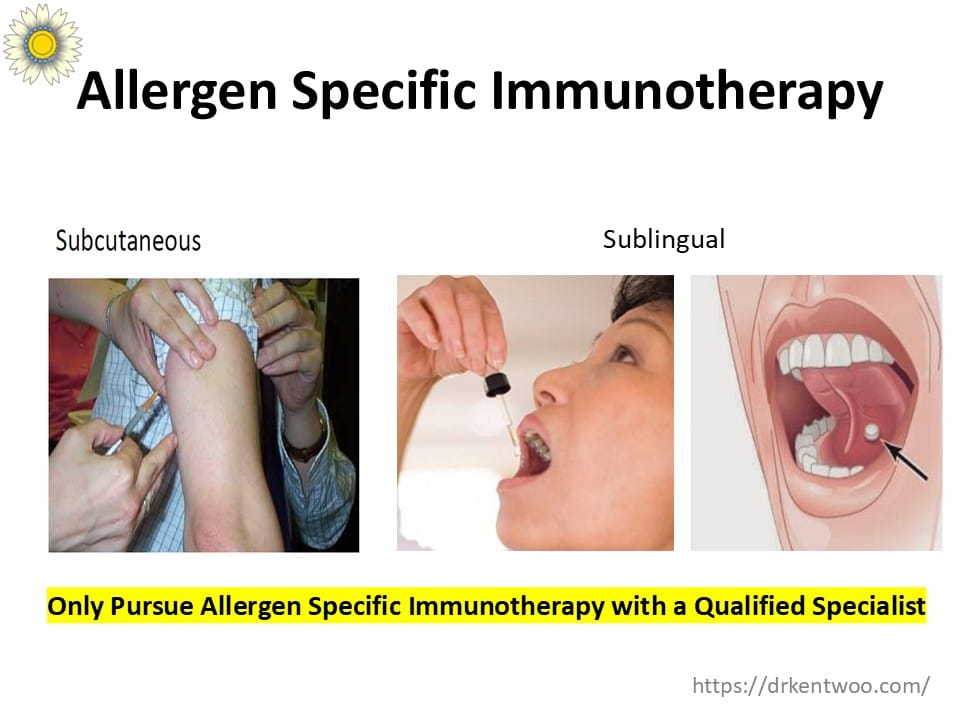
- Injection Immunotherapy (SCIT) – The most effective and well-studied form, given as weekly injections initially, then monthly for 3-5 years.
- Sublingual Immunotherapy (SLIT) – Allergy drops taken under the tongue daily, convenient but less effective for multiple allergies.
⚠️ Warning: Not all immunotherapy is created equal. Immunotherapy should only be prescribed by a trained Allergy & Immunology specialist. Incorrect formulations from unqualified providers may not be effective or safe.
The Missing Piece: The Microbiome’s Role in Allergies

Did you know that your gut bacteria influence how your immune system reacts to allergens? Research shows that an unhealthy microbiome can increase the risk of allergies, while a balanced microbiome can support immune tolerance and reduce allergy severity.
This is why I developed Duoflora, a probiotic designed to complement allergy treatment by strengthening the gut microbiome. It contains:
✅ Bifidobacterium breve M-16V – Helps reduce inflammation, supports skin health, and may lower eczema risk in infants.
✅ Lactobacillus rhamnosus GG – One of the most researched probiotics for allergies, shown to help prevent and manage allergic conditions.
By restoring gut balance, Duoflora supports allergy prevention, immune modulation, and overall health—making it a valuable tool in allergy management.
A Science-Backed Approach to Allergy Management
Allergies affect more than just your nose or skin—they impact daily life, sleep, and emotional well-being. As an immunologist, my goal is to provide families with a clear, science-backed plan to manage and prevent allergies.
By combining prevention strategies, proper treatment, immunotherapy, and microbiome support, we can take a proactive, long-term approach to allergy management—giving families hope and a clear path forward.
If you’re looking for real solutions for allergies, Contact us to create a personalized plan that works for you.